March 2024
Make giant steps towards making ovarian cancer a survivable disease
March is Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month and we’re taking steps for every single woman diagnosed with ovarian cancer worldwide each year. There will also be the launch of new pioneering projects, opportunities to shape the next decade of cancer care and ways to support the next generation of ovarian cancer research.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that affects the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. It can develop when abnormal cells grow in and around the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Anyone who has ovaries can get ovarian cancer, however the chances increase for people over the age of 50. This type of cancer can sometimes be hereditary.
It’s estimated that there are around 4,100 deaths from ovarian cancer in the UK in every year. A rate of one woman every two hours. Because the symptoms are common and misdiagnosed, ovarian cancer is often diagnosed late. The earlier ovarian cancer can be diagnosed, the easier it is to treat.
In this guide we explore:
- What is cancer?
- What are the ovaries?
- What is ovarian cancer?
- Symptoms of ovarian cancer
What is cancer?
Our bodies are made up of billions of cells which are constantly replaced when they are old, damaged, or worn out. To replace a cell, our bodies make a copy of a healthy cell by splitting in two and destroying the old or worn-out cell. Cancer develops when this process of division happens in an uncontrolled and unusual way, resulting in the cell dividing and multiplying until if forms a lump called a tumour.
Tumours can be non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Benign (non-cancerous) tumours do not usually spread to other parts of the body. They may require some treatment but are rarely life threatening. If the tumour is malignant (cancerous), it is cancerous and when left untreated may spread to other parts of the body.
What are the ovaries?
The ovaries are two small glands that form part of the female reproductive system, which is also made up of the vagina, cervix, uterus (womb) and fallopian tubes. Ovaries have two main functions:
- Produce, store, and release eggs for reproduction
- Produce the female sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is the 6th most common cancer in women, with around 7,500 diagnoses each year.
Ovarian cancer starts when abnormal cells in and around the ovary and fallopian tubes grow and divide in an uncontrolled way and form a cancerous tumour (malignant). The cancerous cells grow into surrounding tissues and can spread to other parts of the body.
There are several different types of ovarian cancer and type of cancer depends on the type of cell and tissue the cancer starts in.
Treatment of ovarian cancer will depend on the type, stage and grade of the cancer you’re diagnosed with, however the earlier the cancer is diagnosed the easier it is to treat.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
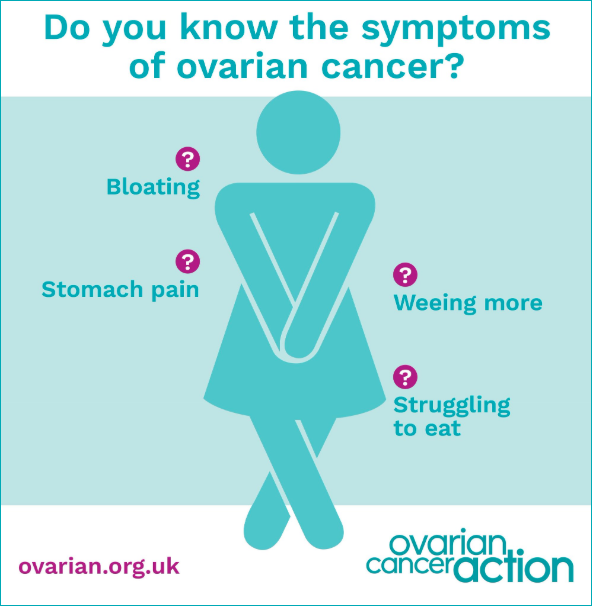
Symptoms of ovarian cancer are common among other, less serious, illnesses such as irritable bowel syndrome. The main four symptoms to be aware of are bloating, stomach pain, difficulty eating and needing to wee more frequently.
Other symptoms such as back pain, changes in bowel habits, extreme tiredness or unexplained weight-loss may also be ovarian cancer symptoms.
Find out more about ovarian cancer symptoms and what to do if you’re experiencing them.
